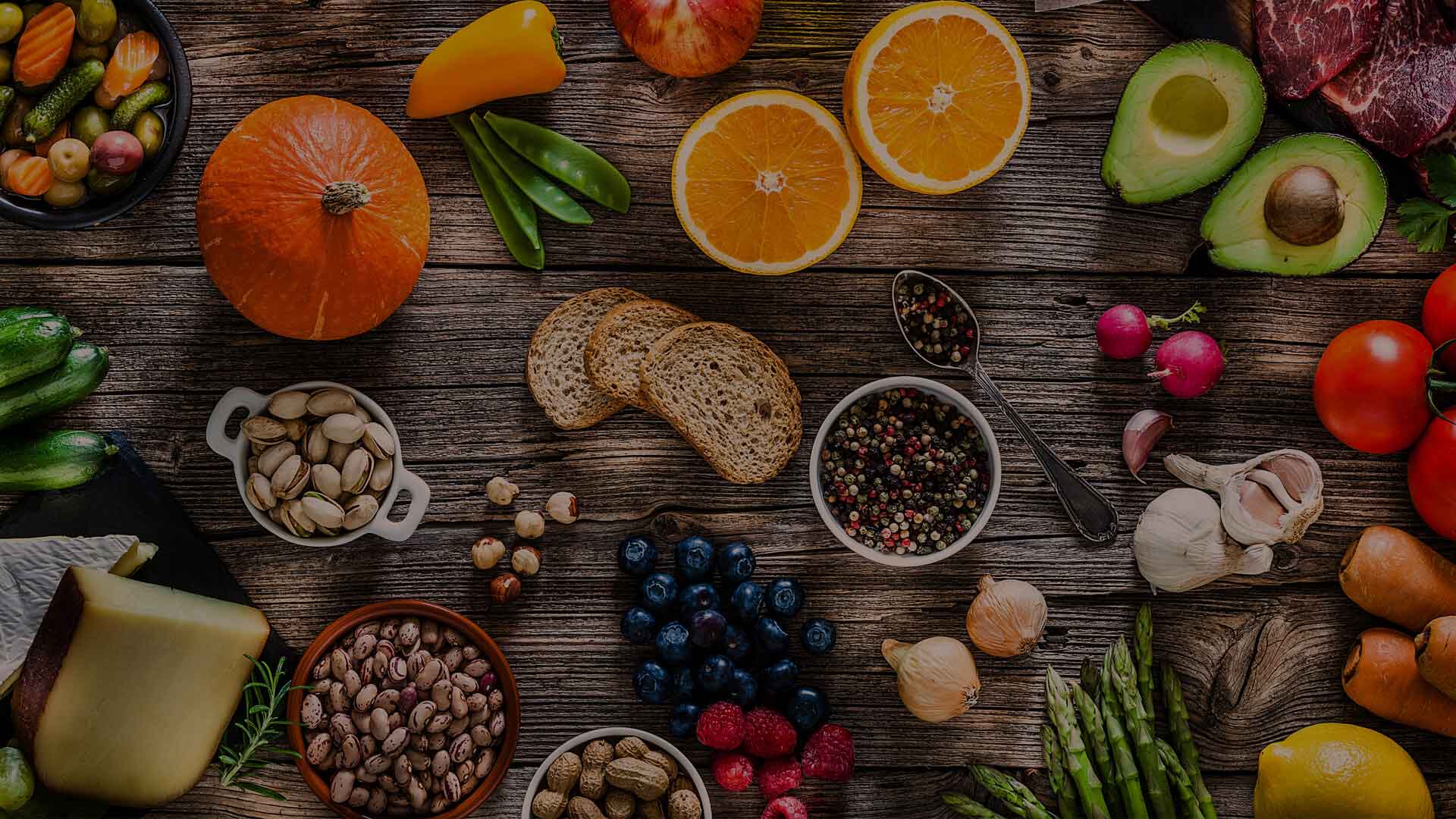
Fruits
Nutritional Interventions
- Increased intakes of protein ,carbonates , energy and fluids is recommended.
- Feeding via a catheter is recommended in circumstances of weightloss, decreased apetite, dehydration or electrolyte disorders.
- The diet should be amended depending on the apparent unwanted actions. Also, the sufficient intake of vitamins and minerals should originate from food. Providing a special diet, it is possible to ameliorate the intake of vitamins and energy while decreasing weight loss and making the quality of life better.
- Small and frequent meals can be beneficial
- If nutrition via the mouth is possible, it should include: citrus fruits, vegetables, sesame, walnuts (because they contain gamma-tocopherol), apples, onions (they contain quercetin), and other flavonoids.
- Selenium, lycopene, carotenoids as well as natural estrogens (such as soya products) are also recommended. Curcumin as seasoning, as long as it is tolerated can be used.
- The consumption οf phytosterols from sunflower seeds, pistachios, sesame and wheat plant is recommended.
- The intake of omega-3 fatty acids from fish, shellfish , flaxseed and walnuts.
- Resveratrol from red wine and berries is shown to be beneficial however the levels of tolerance should be examined every time.
Dietary sources of protein
Chicken, fish, tuna packed in water, steak, cheese, meat, pork, low fat yogurt, lentils, skim milk, fava beans, peas, beans, soy milk, egg, whole wheat bread, broccoli, nuts, cooked potato, corn, cooked cereals or rice or pasta.
Dietary plant sources of protein
Tofu, soya, lentils, peas, cooked pasta, soy milk, almond milk, whole wheat bread, broccoli, nuts, baked potato, corn, and rice.
Sources of tryptophan
Lean meat – skinless turkey, skinless chicken / Dairy – yogurt, eggs, graviera, cottage cheese / Nuts – almonds, hazelnuts, pistachios / soy / Seeds – pumpkin seeds, sesame / Legumes- lentils, chickpeas (hummus) /Vegetables- spinach, watercress, cabbage / whole grain – oats, brown rice, paximadi / Fruits – banana, pineapple, plums, figs.
Sources of tyrosine
Lean meat – turkey, tuna, chicken liver, beef liver / Dairy – Cheddar, emmental, graviera, mozzarella, parmesan, Swiss cheese / avocado / green beans – soy sauce, spinach, marmite, Fruits- bananas, canned figs, plums, raisins, tomatoes, plums.
Dietary sources of Ω3 fatty acids
Soybean oil / flaxseed / soybean / pumpkin seeds / seed oil / walnuts. Flaxseed should be consumed within 24 hours of grinding. Fatty fish and seafood, such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring, trout, sardines. Dark green vegetables and fortified with Ω-3 foods.
Main dietary sources of carotenoids
The bioavailability of carotenoids from vegetables is low, fat is essential for adequate absorption. Between 9 and 17 % of carotenoids are absorbed. People with an increased risk of developing lung cancer (e.g. smokers and workers exposed to asbestos) should not take Β-carotene supplements. B-carotene is found in deep yellow, orange, or dark green fruits and vegetables such as pumpkin, sweet potatoes, carrots, spinach, cabbage, turnips, melon, apricots, lettuce, broccoli, papaya, mango and mandarin. Red and green pepper, tomato, watermelon.
Dietary sources of lycopene
Tomatoes and tomato paste, watermelon, grapefruit, asparagus, pomegranate, cherries, red onions, red peppers.
Dietary sources of selenium
Seafood and shellfish such as: sardines, shrimp, crabs, tuna, pink salmon (canned), liver, red meat, pork, whole grains and seeds (their selenium content depends on the selenium content of the soil), Brazilian nut egg, chicken, bulgur oatmeal.
Herbs and nutritional supplements
The use of complementary and alternative medicine by patients with lung cancer is widespread. Doctors should judge each time to avoid any side effects and interactions with conventional treatments. Beta-carotene supplements should be avoided. The diet has more protective properties. Research data examines the consumption of garlic and the intake of selenium, N-acetyl-cysteine, vitamins B6 and C.
